API for Other Mods
API for Other Mods
The Fabric version of Immersive Portals mod contains some API for other mods to use.
API Overview
Start from mod version 5.0.0 (Mc version 1.20.4), this mod becomes one mod.
When the mod is only provided by jar-in-jar, the default config of "nether portal mode", "end portal mode" and "enable mirror creation" will be respectively vanilla, vanill and false. This means that if this mod is only provided by jar-in-jar, and no existing mod config file exists, it will not change any existing vanilla behavior by default.
The dimension API now has been moved to DimLib.
For MC 1.16 - 1.20.2
Old versions of Immersive Portals mod's is split as 3 mods:
- Immersive Portals Core (
imm_ptl_core). It allows adding and managing see-through portals. It also enables the client to load multiple dimensions at the same time. It also contains chunk loading facilities. It requires both client and server to install. - Miscellaneous Utility Library from qouteall (
q_misc_util). It contains the dimension API and some utilities. It allows dynamically adding and removing dimensions without restarting the server. It can work as server-only (if the client does not install it, the command completion of dimension id won't be updated). - The outer mod. Contains nether portal, end portal and dimension stack functionality.
Both imm_ptl_core and q_misc_util will not change vanilla behavior by default.
Here is the brief documentation of the API. You can also refer to the JavaDoc in code. If you have any question using the API, you can contact qouteall via discord or open a discussion.
Code examples: MiniScaled mod and Portal Gun mod use Immersive Portals API.
Immersive Portals API (imm_ptl_core)
Create a Portal
Example:
The portal can face any rotation, be anywhere, point to any position in any dimension.
It's recommended to check Portal Attributes .
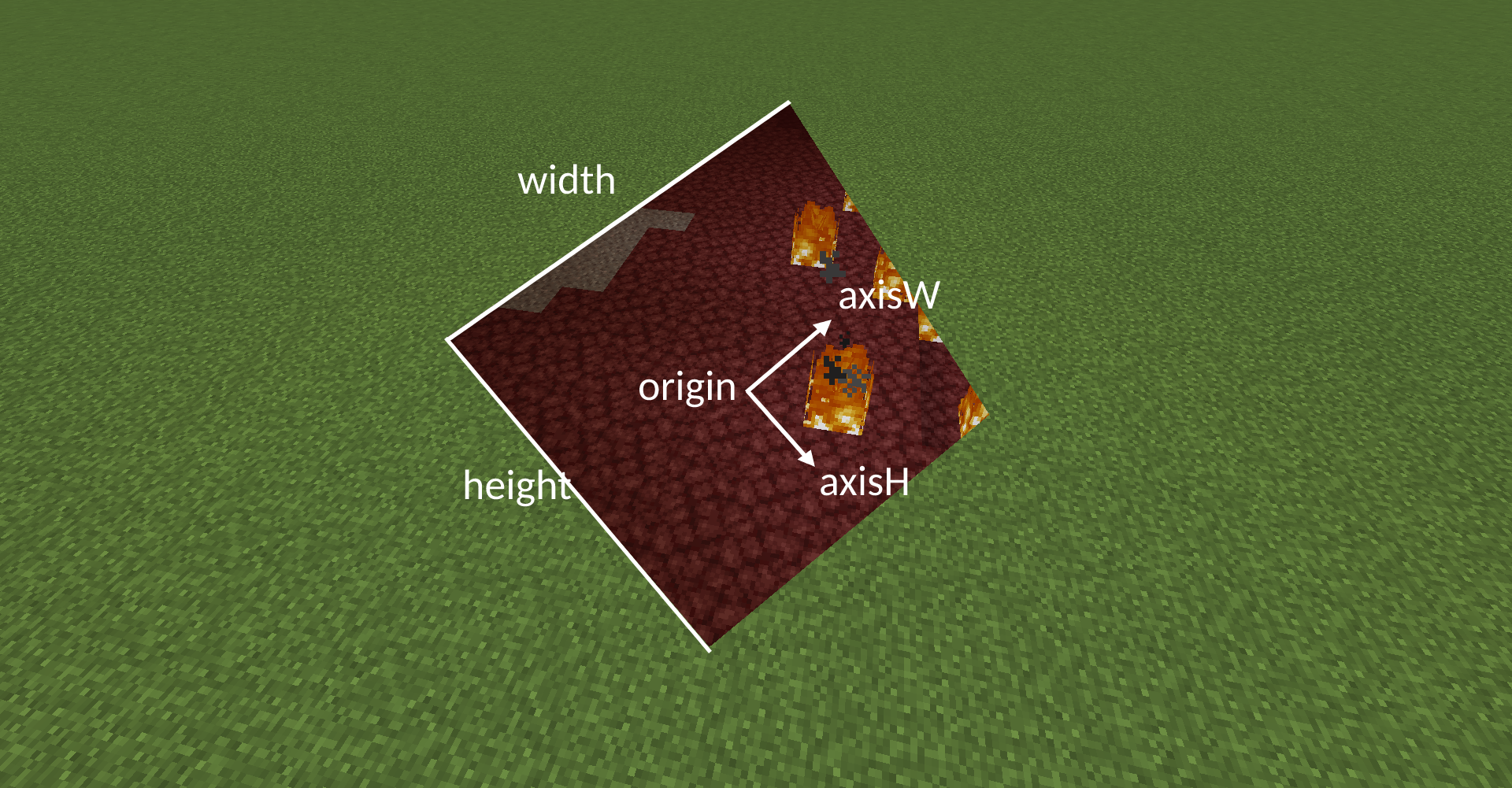
axisW and axisH are unit vectors and should be perpendicular to each other. The portal orientation has nothing to do with pitch and yaw (because pitch and yaw cannot represent tilted rotations).
If the portal attribute gets changed on the server side after the portal has spawned, call portal.reloadAndSyncToClientNextTick() to sync the changes to client.
To create the reverse/flipped portal entity, use PortalAPI.createReversePortal PortalAPI.createFlippedPortal . How bi-way portals and bi-faced portals are organized
About Rotations and Quaternions
You can set the portal's rotating transformation by setRotation() . The rotation transformation is represented using quaternion. Minecraft uses Quaternionf which is mutable. iPortal uess its own DQuaternion which is immutable.
A quaternion is a rotating transformation. For example you can create a rotation along Y axis for 45 degrees by DQuaternion.rotateByDegrees(new Vec3(0, 1, 0), 45).toMcQuaternion() .
About quaternions, you just need to know these:
- A quaternion can be seen as a unit 4D vector. If the 4D vector is not unit-length, it will not be a valid rotation.
- Hamilton product combines two rotating transformations.
a.hamiltonProduct(b)gives the rotation that firstly applyband thena. The sequence matters. - Conjugate means getting the inverse rotation.
- Having the 4 numbers negated does not change the corresponding rotation.
- The quaternion can be interpolated on the 4D sphere surface.
Quaternion can not only represent a rotating process, it can also represent an orientation. You can manipulate portal orientation by PortalAPI.getPortalOrientationQuaternion and PortalAPI.setPortalOrientationQuaternion .
iPortal does not use Euler angle for rotation because Euler angle requires handling many edge cases. Quaternion is less intuitive but easier to interpolate and multiply.
Creating a Subclass of Portal and a New Entity Type
For example, if you want to add a subclass of Portal: XPortal
Chunk Loading API
Vanilla has the force-load functionality but it only loads the chunk and does not synchronize the chunk to player client. This mod supports loading chunks and synchronize the chunk (blocks, entities, etc.) to the specific player.
Example:
After adding the chunk loader, you probably need to store the ChunkLoader object reference, and call removeChunkLoaderForPlayer when you want to stop loading (Note: in the latest version, it removes chunk loader by reference, not value).
Access Multiple Client Worlds
This mod eliminates the limitation that only one dimension can be loaded on client at the same time. If you want to get the nether world, use ClientWorldLoader.getWorld(Level.NETHER) . The client world will be created when it's used at the first time.
If the client experiences conventional dimension change (with loading screen) then all worlds will be unloaded and recreated later.
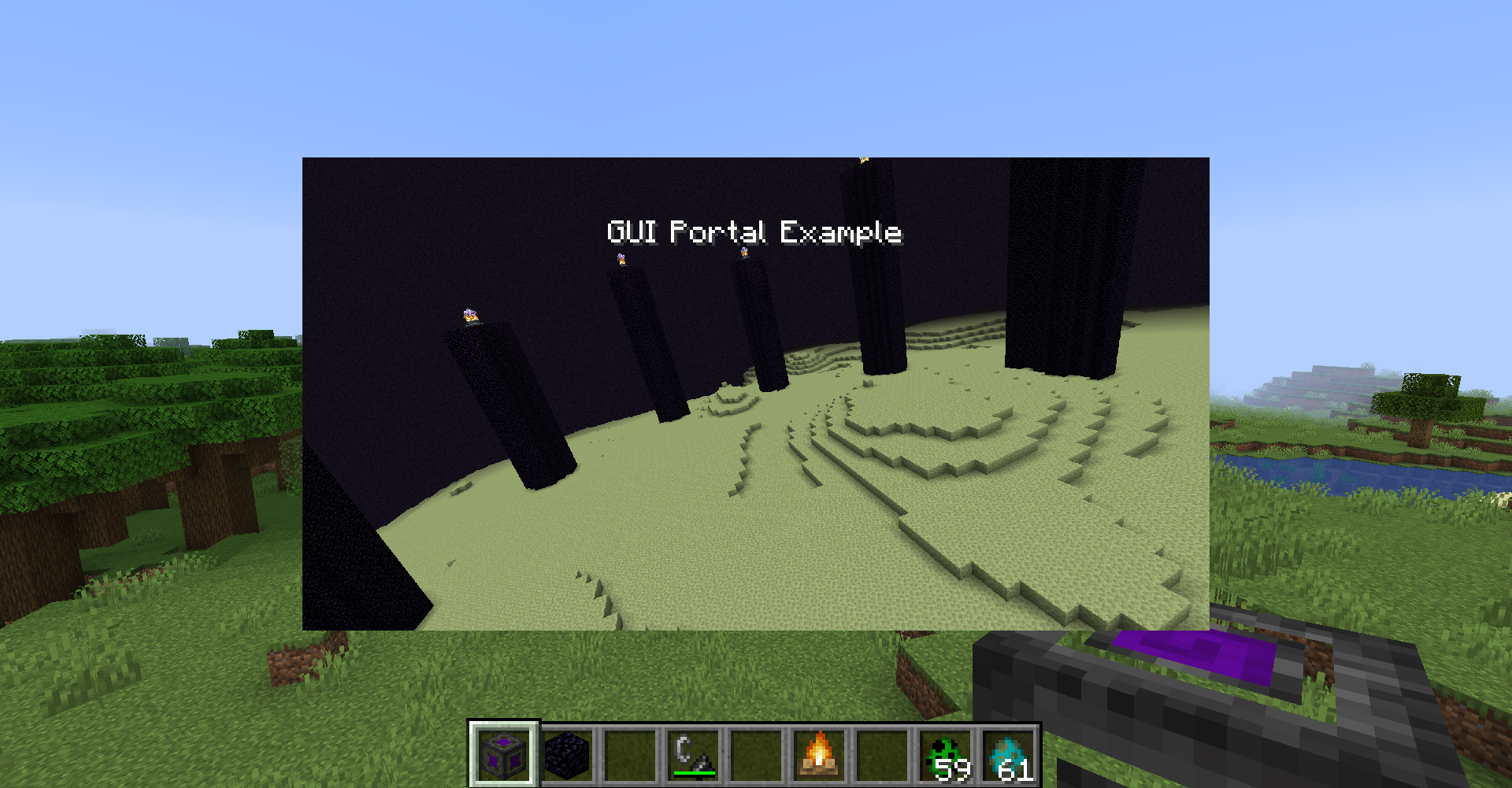
GUI Portal
Use GuiPortalRendering.submitNextFrameRendering(worldRenderInfo, frameBuffer) to ask it to render the world into the framebuffer in the next frame. The rendered dimension, position, camera transformation can be specified in the WorldRenderInfo.
That framebuffer will automatically be resized to be the same size as the game window.
Networking Utility (Remote Procedure Call)
The remote procedure call utility allows easier networking communication (without writing packet type and serialization/deserialization code for eacy packet type).
Example: if you want the server to send a packet to ask the client to invoke this method (on the render thread):
public class AAARemoteCallableBBB{
public static void clientMethod(int arg1, double arg2) {...}
}
Do this
McRemoteProcedureCall.tellClientToInvoke(
player,
"path.to.the_class.AAARemoteCallableBBB.clientMethod",
3, 4.5
);
If you want the client to send a packet to ask the server to invoke this method (on the server thread):
Do this
McRemoteProcedureCall.tellServerToInvoke(
"path.to.the_class.AAARemoteCallableBBB.serverMethod",
Blocks.STONE
);
For security concerns, the invoked method's class path must contain "RemoteCallable". For example, the class name can be "XXRemoteCallableYYY" or "RemoteCallables".
The supported argument types are
- The types that Gson can directly serialize/deserialize, including
int,double,boolean,long,String,int[],Map<String,String>, Enums, Plain old java objects
and:
Using unsupported argument types will cause serialization/deserialization issues.
Note: the packet handling code should validate packet content, including checking permission and checking position.
How to Make Other Mod's Portals See-through
Immersive Portals' datapack-custom-portal system allows converting a conventional portal (a portal that is similar to nether portal, for example the portal of Paradise Lost) to see-through when the player goes through the portal. That JSON file can be directly put into the mod jar. Example in Paradise Lost mod. If the mod author did not put the conversion generation file into the mod jar, you can also use your own datapack to add it.
It converts when after the player goes through portal once. The portal is not converted when lighting the portal because iPortal didn't know how to select the destination and generate the frame, until the player goes through the portal once.
Configure Dependency in Fabric
In your build.gradle:
Possible Sources of Mod Incompatibility with Immersive Portals
Immersive Portals mod deeply changes game mechanics and eliminated a lot of vanilla restrictions, so it may be incompatible with some mods in these ways:
The mod that's developed based on the fact that only one dimension is loaded on client may be incompatible with ImmPtl.
The latest version of ImmPtl does not change the player's dimension, so the mod can compare the Level with player.level() to know whether it's rendering or ticking the dimension that the player is not in.
For the mods that store per-dimension data on client, making the data attached to Level(World) or LevelRenderer (WorldRenderer) may solve the issue.
The networking packets to client does not include the dimension information, so ImmPtl wraps some packets as "redirected packet" to attach dimension information. For the mods that send synchronization packets to client, for example, sending packets to synchronize custom data of entity or block entity, it may fail to find the entity or block entity in the current Level because that packet is not redirected. The mod can choose to use Cardinal Components to sync the additional data (ImmPtl has special code to make Cardinal Components packet redirected).
Dimension API in DimLib
Before mod version 5.0.0 (MC version 1.20.4), the dimension API is in q_misc_util. The documentation of the dimension API of old versions is here.
Not the dimension API is in DimLib.
Dynamically Adding and Removing Dimensions
Add and remove a new dimension dynamically:
When creating a new ChunkGenerator, you can use the content from the RegistryAccess. The added dimension's configuration will be saved into level.dat file. The chunk generator need to have a working codec.
The added dimension's id should not duplicate with existing dimension. You can use DimensionAPI.addDimensionIfNotExists to avoid adding dimension if the dimension with that id already exists.
Removing a dimension does not delete its world saving file.
Adding Dimensions During Server Initialization
Sometimes you want to add a new dimension during server startup, but want to add dimension based on config file or some other dynamic things, so the dimension cannot be hardcoded in JSON, then you can do this:
DimensionAPI.SERVER_DIMENSIONS_LOAD_EVENT.register(server -> {
DimensionAPI.addDimensionIfNotExists(...);
});
Register Codec for Custom Chunk Generator
TODO
